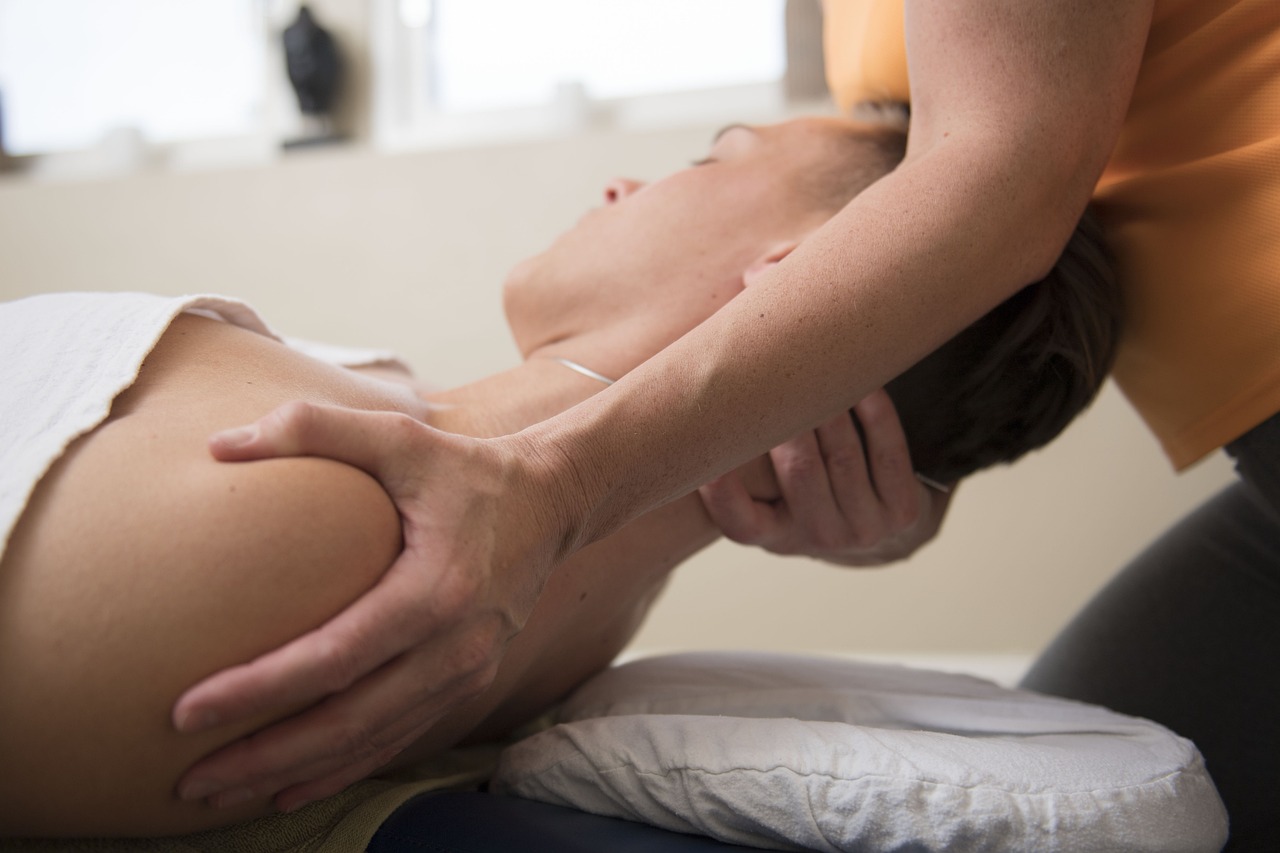
Purpose of Prone knee bend test 2: To determine if the tension along the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve contributes to the neurologic symptoms associated with radiculopathy (1, 2).
Patient position: Prone lying.
Examiner position: Standing beside the patient, at the side of the limb to be tested.
Procedure: Perform the limb/joint positioning sequence in the following order:
- Neutral alignment at the lumbar and thoracic spine, while the patient is on prone lying,
- Cervical spine rotation to the test side (3, 4),
- Knee flexion (with the examiner’s one hand around the patient’s ankle),
- Hip extension (slightly about 10 – 20 degrees, with the examiner’s other hand holding the patient’s flexed knee),
- Sensitizing position: Hip in the neutral position to slight extension (5).
Outcome: This test is positive if (a) the limb/joint positioning sequence reproduces symptoms associated with radiculopathy, (b) the sensitizing position reproduces symptoms, and (c) there is a repeatable and measurable asymmetry between both sides along with the reproduction of symptoms.
Reference:
- Butler DS, Matheson J. The Sensitive Nervous System: Noigroup Publications; 2000.
- Kopell HP, Thompson WAL. Peripheral entrapment neuropathies: Williams & Wilkins; 1963.
- Magee DJ. Orthopedic Physical Assessment: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013.
- Butler DS, Jones MA, Gore R. Mobilisation of the nervous system: Churchill Livingstone Melbourne etc.; 1991.
- Loudon JK, Swift M, Bell S. The Clinical Orthopedic Assessment Guide: Human Kinetics; 2008.