How to Pinpoint Hip Joint Pain: Unlocking the Secrets of Diagnosis
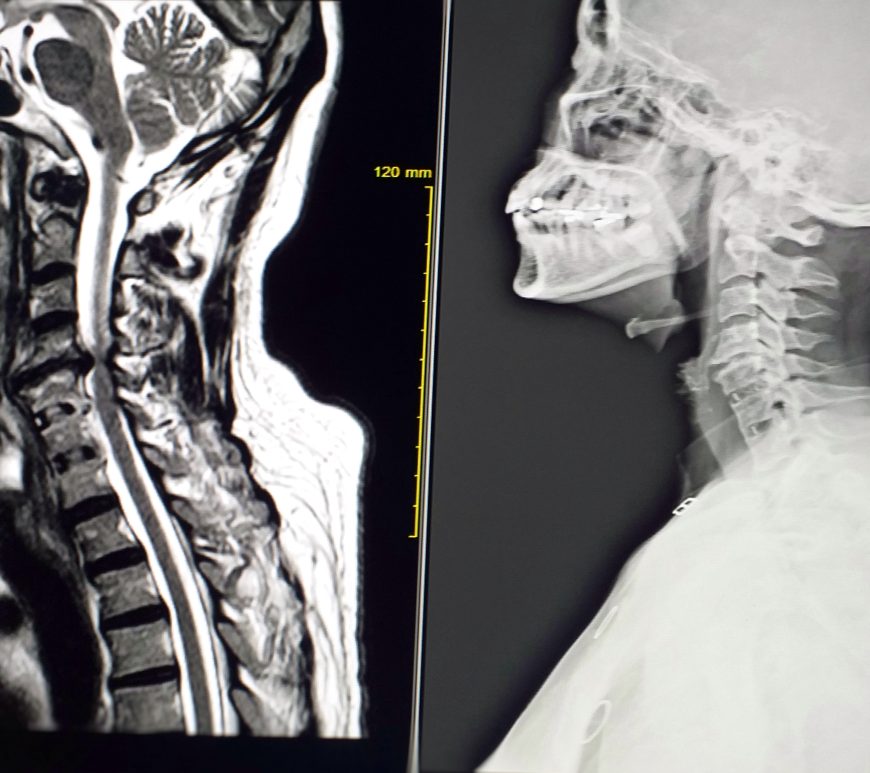
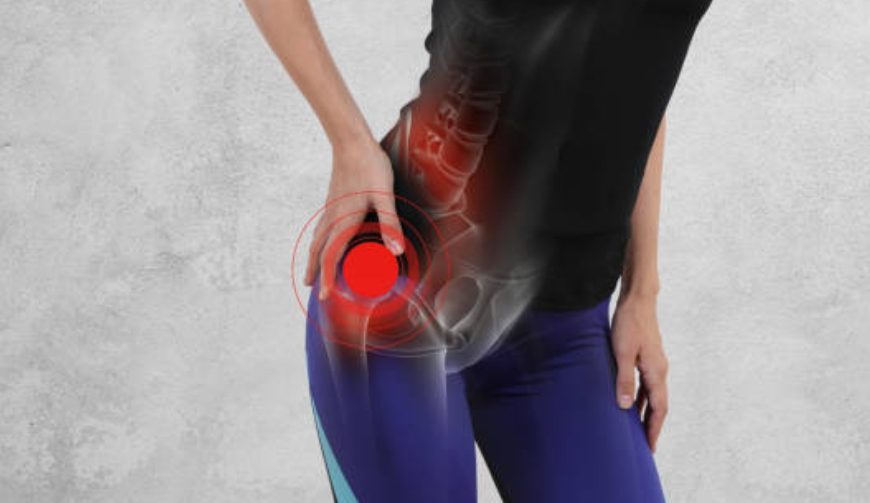
Hip pain can have multiple causes, including non musculoskeletal, lumbosacral spine, intra-articular, and extra-articular. A consensus declaration has defined an evaluation algorithm for distinguishing the musculoskeletal causes of regional hip pain (Takla A et al. 2020). Lumbosacral and extra-articular diseases frequently coexist with intra-articular hip causes of pain (Takla A et al. 2020). As a result, a grasp of the complicated connections of the spine, … Continue reading How to Pinpoint Hip Joint Pain: Unlocking the Secrets of Diagnosis